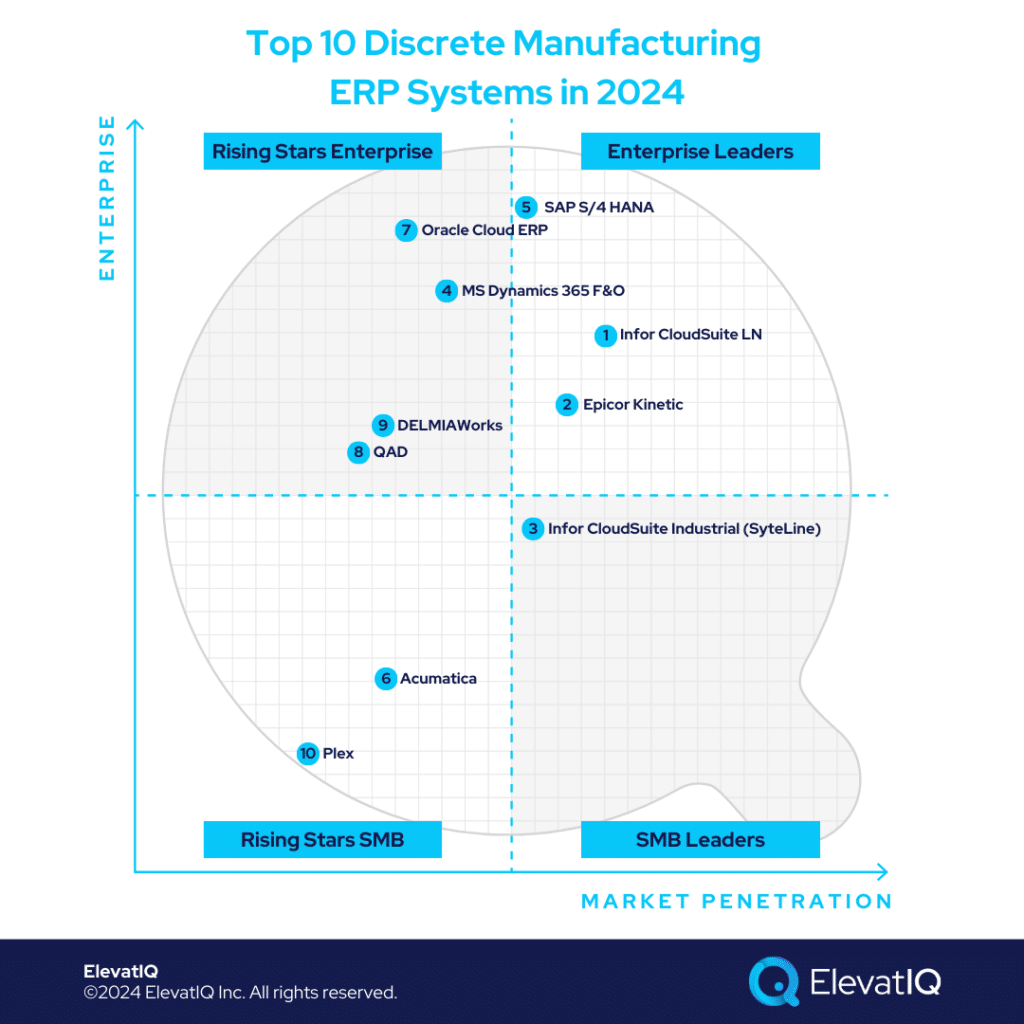
Top 10 Discrete Manufacturing ERP Systems In 2024
Discrete Manufacturing Companies. Producing distinct items manufactured through a series of assembly processes, where individual components are combined to create the final product, discrete manufacturing typically involves BOMs, assembly lines, and detailed production schedules. The process results in tangible, countable products that can be individually tracked and managed through the supply chain. This type of manufacturing contrasts with process manufacturing, which produces goods in bulk, like chemicals or beverages, where the end products are not discrete items but rather homogeneous outputs.
Discrete Manufacturing Processes. It involves the production of distinct, countable items through a series of assembly and fabrication steps. These processes include assembling components, machining, welding, and quality testing, often organized along assembly lines. Each step in the process is distinct and can be tracked individually, with a focus on precision and customization. This approach is commonly used in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and machinery.
Discrete Manufacturing ERP Needs. Modules for managing production planning, inventory control, and supply chain coordination are of utmost importance in this case. These systems must support detailed tracking of parts and components, facilitate efficient scheduling and resource allocation, and provide real-time visibility into production processes. Additionally, they require strong capabilities in quality management, engineering change control, and compliance tracking to handle the complexities of producing distinct items. Integration with CAD systems, advanced analytics for performance monitoring, and flexible reporting tools are also essential to address the unique demands of discrete manufacturing. So, which are the leading discrete manufacturing ERP systems for 2024?

Criteria
- Definition of a discrete manufacturing company. These companies in the discrete manufacturing ecosystem include manufacturers that follow discrete manufacturing processes producing products in industries such as Automotive, Aerospace, Industrial, and Machinery. From the manufacturing mode types, they could belong to any of the categories such as make-to-order, make-to-stock, engineer-to-order, or project manufacturing. The list considers companies of all sizes in this ecosystem.
- Overall market share/# of customers. The higher marketshare among discrete manufacturing companies drives higher rankings on this list.
- Ownership/funding. The superior financial position of the ERP vendor leads to higher rankings on this list.
- Quality of development. How modern is the tech stack? How aggressively is the ERP vendor pushing cloud-native functionality for this product? Is the roadmap officially announced? Or uncertain?
- Community/Ecosystem. How vibrant is the community? Social media groups? In-person user groups? Forums?
- Depth of native functionality. Last-mile functionality for specific industries natively built into the product?
- Quality of publicly available product documentation. How well-documented is the product? Is the documentation available publicly? How updated is the demo content available on YouTube?
- Product share and documented commitment. Is the product share reported separately in financial statements if the ERP vendor is public?
- Ability to natively support diversified business models. How diverse is the product in supporting multiple business models in the same product?
- Acquisition strategy aligned with the product: Any recent acquisitions to fill a specific hole for discrete manufacturing industries? Any official announcements to integrate recently acquired capabilities?
- User Reviews: How specific are the reviews about this product’s capabilities? How recent and frequent are the reviews?
- Must be an ERP product: Edge products such as HCM, CRM, eCommerce, MES, or accounting solutions that are not fully integrated to support enterprise-wide capabilities are not qualified for this list.
10. Plex
Adopting an MES-first strategy, Plex targets companies in the Toyota and Ford automotive ecosystems. Despite superior technology compared to other solutions on this list, Plex has fewer installs, primarily focusing on the automotive industry. Uniquely, Plex integrates some of the HCM processes tightly with MES and ERP, which is beneficial for automotive companies if skillsets and certifications are key inputs for production scheduling. However, its relevance may vary for other industries. Given its pros and cons, it maintains the #10 spot among the top 10 discrete manufacturing ERP systems.
Strengths
- MES-first approach. Plex excels with its MES-first architecture, which is particularly strong for shop-floor heavy industries.
- Stronger automotive last-mile compliance capabilities. Plex offers deep last-mile and compliance capabilities for automotive companies and other MES-intensive industries.
- Cloud-native. Plex’s technology is superior due to its cloud-native origins, setting it apart from other systems.
Weaknesses
- Weaker ERP layers. Plex’s ERP capabilities and integration layers are not as robust, leading to potential challenges in adapting to various business transactions and models.
- Not as scalable for diverse business models. The ERP may face difficulties scaling to accommodate different business models, affecting its flexibility.
- Limited ecosystem and consulting base. Being more prescriptive, Plex has a weaker ecosystem and consulting base compared to other ERP solutions.
9. DELMIAWorks
DELMIAWorks has performed really well from an industry perspective, particularly in more process-centric sectors such as plastics. Industries related to plastics, especially from a discrete perspective, will benefit significantly from DELMIAWorks. Additionally, it has a tighter alignment with the CAD system SolidWorks. Industries using SolidWorks will experience richer capabilities and superior alignment from a product capabilities perspective. Therefore, the industries to consider for DELMIAWorks include automotive and aerospace, especially if they are slightly more plastic-centric within those verticals. This contributes to the placement of this product at #9 spot in our list of top discrete manufacturing ERP systems.
Strengths
- Seamless integration with other tools in SolidWorks portfolio. Their alignment with the CAD system SolidWorks is particularly noteworthy. Industries utilizing SolidWorks can expect seamless integration and superior alignment.
- Discrete and process manufacturing capabilities. Ideal for industries, that primarily focus on discrete manufacturing, but may also incorporate process manufacturing lines. This scenario is common in packaging-centric or medical device-centric industries.
- Supply chain best-of-breed solutions as part of the suite. The suite comes fully equipped, pre-baked, pre-configured, and pre-integrated, saving you the hassle of investing heavily in these aspects as required by other solutions. These capabilities are typically sourced from third-party providers.
Weaknesses
- Legacy technology. The technology is not as cutting-edge. They haven’t invested as heavily as some of their competitors in modernizing their systems. Even vendors who entered the field later have announced plans to upgrade to cloud-native technology stacks, a move that DELMIAWorks has not yet made. As a result, their technology remains somewhat outdated and legacy-like.
- Not as scalable for all discrete industries. The scalability of DELMIAWorks may not be suitable for all discrete industries, particularly if your business model is complex. In such cases, where there are multiple layers across various industries, you might encounter challenges.
- Limited ecosystem and consulting base. The consulting base and ecosystem for DELMIAWorks are comparable to Plex, with limitations due to the nature of the prescriptive category they belong to.
8. QAD
QAD targets mid-to-large discrete manufacturing companies such as automotive, electronics, and life sciences companies with a depth in the supply chain. It’s especially suitable for discrete companies that require deep layers of collaboration with their vendors for forecasting and planning. It excels in commoditized, consumer-centric products. These industries are strong from a supply chain planning perspective, and QAD offers superior capabilities as part of its suite. This is because, for these industries, supply chain capabilities are highly intertwined. But it’s not a fit for companies with diverse business models or very small companies. QAD has seen substantial advancements in its portfolio, especially with its technology, which was a massive barrier for QAD in the past. Thus, contributing to the placement of this product at #8 spot in our list of top discrete manufacturing ERP systems.
Strengths
- Supply chain suite + ERP as part of the suite. QAD excels in offering superior capabilities within its suite, especially in terms of supply chain and ERP functionalities. This is particularly advantageous for discrete industries like automotive, where these capabilities are deeply interconnected and essential components of the suite.
- Discrete companies with process manufacturing lines or components. Quite similar to those of DELMIAWorks. Both solutions offer integrated discrete and process manufacturing capabilities within their suites. However, the specific focus and target industries of QAD differ from those of DELMIAWorks. Also, the manufacturing processes they cater to and the industries they serve have distinct differences.
- Global capabilities. QAD also has strong global capabilities. If your company requires processes such as in-depth collaboration, which is very common in supply chain companies, then QAD is a great fit.
Weaknesses
- New technology might not be stable or rolled out to all modules. Even though they have announced that they are upgrading their technology, it might take a few years before this version becomes stable. Initially, there will be some modules that may not be fully developed. These incomplete modules could pose challenges during ERP implementation.
- Ecosystem. The ecosystem or consulting support will not be as strong because this is a slightly more prescriptive category.
- Not as diverse. This is not a good fit for companies with hybrid business models as the data and process model is highly tailored for specific discrete verticals.
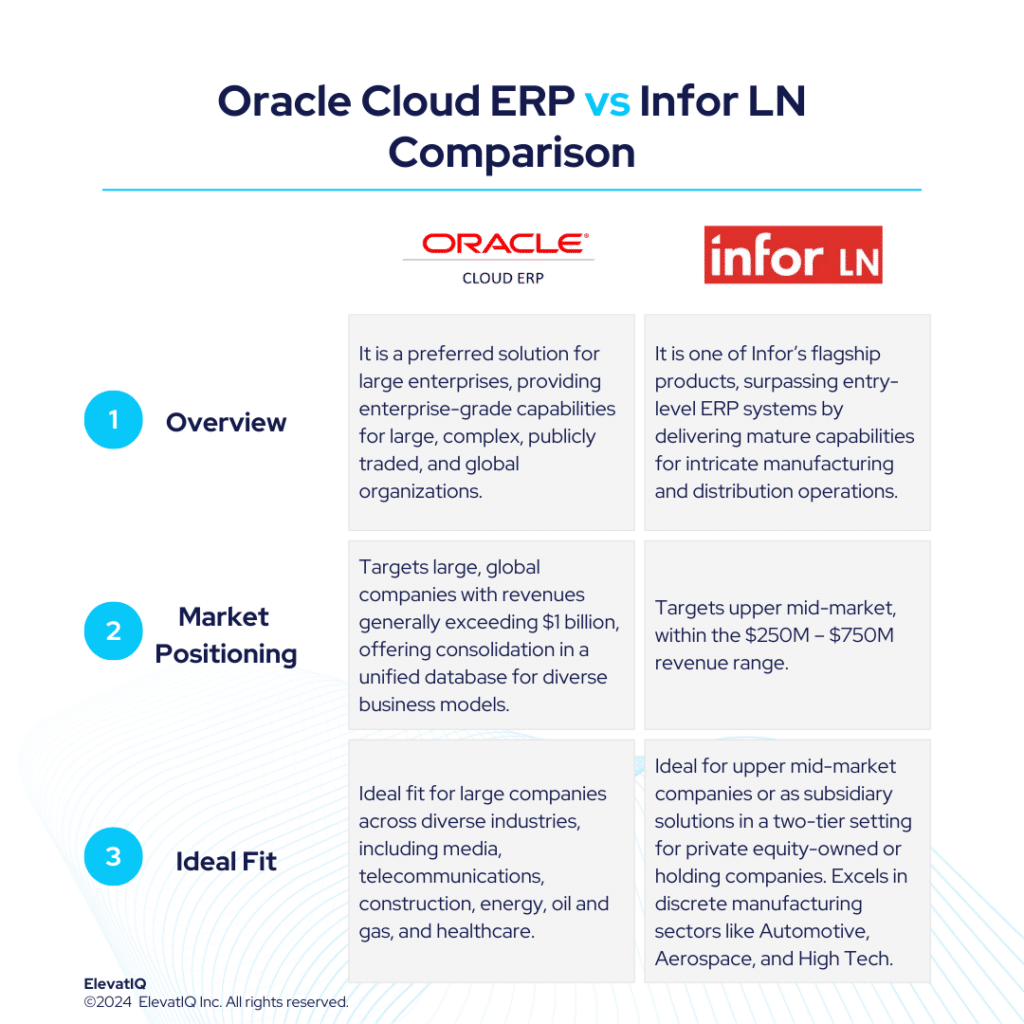
7. Oracle Cloud ERP
Geared toward large discrete manufacturing firms with 10+ global locations (over $1B in revenue), Oracle Cloud ERP excels with high transaction volumes. Ideal for companies prioritizing financial functionality over plant-level needs or preferring plant-level integration with best-of-breed solutions. It is not the optimal choice for SMB discrete manufacturers lacking internal IT capabilities seeking full-suite capabilities. Oracle Cloud ERP is also ideal for global companies with diverse business model that plan to use multiple ERP systems at the plant level and use Oracle Cloud ERP as their corporate ERP system. Thus, contributing to the placement of this product at #7 spot in our list of top discrete manufacturing ERP systems.
Strengths
- ERP layers for complex organizations. This ERP system is designed for large global publicly traded companies. These companies typically require international financial consolidation and aim to integrate various business models and geographies into one solution. This is necessary to ensure end-to-end traceability.
- Diversity of the solution supports most discrete industries. The ERP layers are highly adaptable and designed to support various business models, resulting in a very diverse product. In contrast, other products may not offer the same level of diversity.
- Global compliance and localization. They will be supported in many different countries, whereas prescriptive solutions may not have such extensive support.
Weaknesses
- Last mile capabilities through third-party vendors. The last mile capabilities, especially the suite integration will often come through third-party vendors. This introduces vendor risk, as these third parties may not always be as well-audited or documented.
- Expensive implementation. In general, the implementation tends to be more expensive due to the involvement of multiple vendors. You also have to manage several different integrations, which might be pre-baked in other systems. Since this is a larger product, it will require significantly more time to implement.
- Requires a mature internal IT team. In tailoring, customizing, and configuring these capabilities, the same capabilities that are already included as part of the suite, Oracle Cloud ERP also requires a very mature internal IT team.
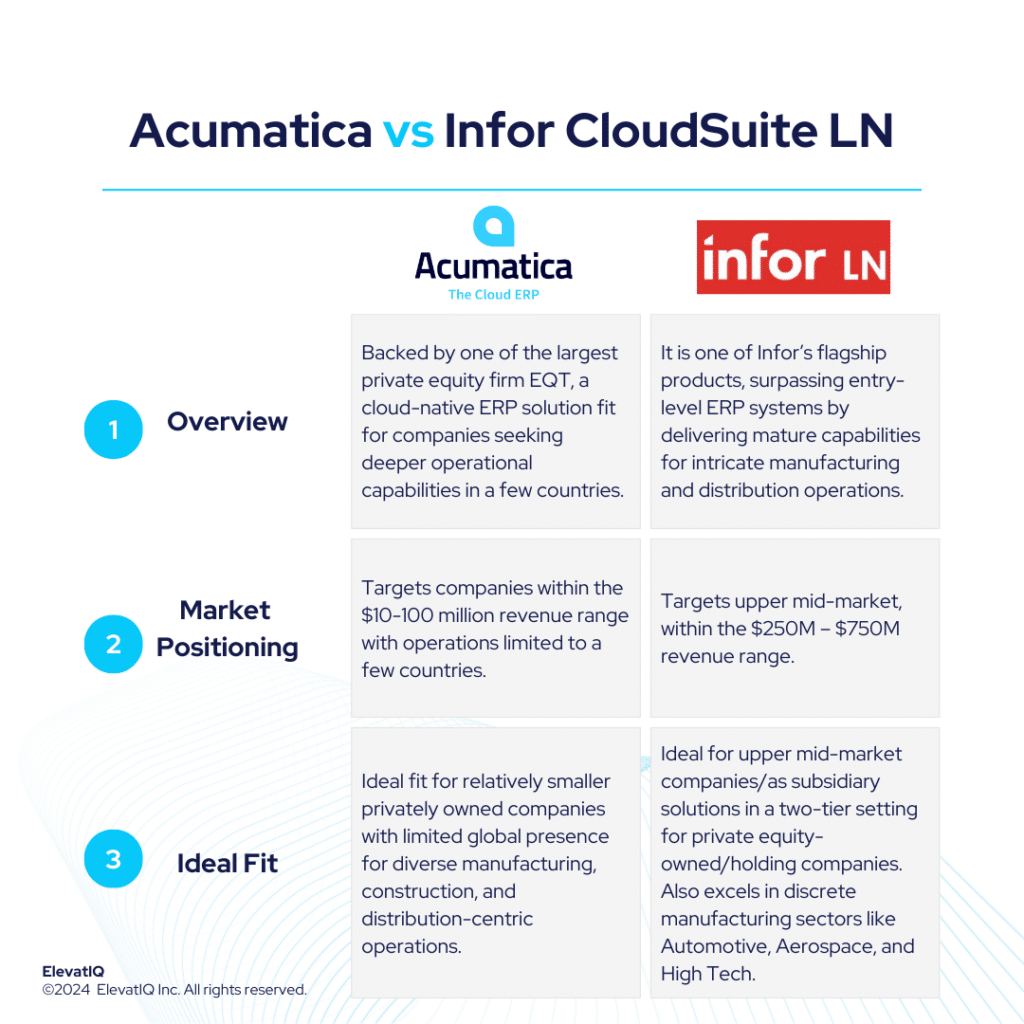
6. Acumatica
Acumatica is a better fit for smaller discrete manufacturing companies, primarily located in countries such as the US, Canada, the UK, and Australia. These companies often require deeper operational capabilities and may not prioritize financial consolidation. It is acceptable to keep different countries in separate instances, as there may not be significant operational or financial synergies between these companies. With limited global operational capabilities, it may not be ideal for those seeking shared services or global synergies. Nevertheless, smaller discrete manufacturing startups valuing a superior user experience would find Acumatica appealing. Thus, contributing to the placement of this product at #6 spot in our list of top discrete manufacturing ERP systems.
Strengths
- Discrete companies requiring CPQ and field services capabilities. It can accommodate several different business models—field service, distribution, manufacturing, and construction—all within the same product and database. This allows for far greater traceability among these business processes, eliminating the need for them to be siloed from an overall capabilities perspective.
- Technology. The technology is superior to some of the legacy products especially when discrete companies might care for capabilities such as enterprise search or mobility.
- Ideal for seasonal discrete companies. It would also be a great fit for seasonal companies because of consumption-based pricing. For example, school supply manufacturing business, or construction, manufacturing businesses, etc.
Weaknesses
- Not native process manufacturing. The solution lacks native support for process manufacturing capabilities for discrete companies with hybrid business models. Although third-party add-ons are available, it can introduce the challenge of dealing with different vendors and their associated legal and technical risks.
- Not a native quality module. They lack a quality module owned by Acumatica, meaning you’ll need to rely on another add-on vendor to address this gap.
- Limited global consolidation capabilities. Acumatica has limited global capabilities for discrete companies seeking synergies among global entities.
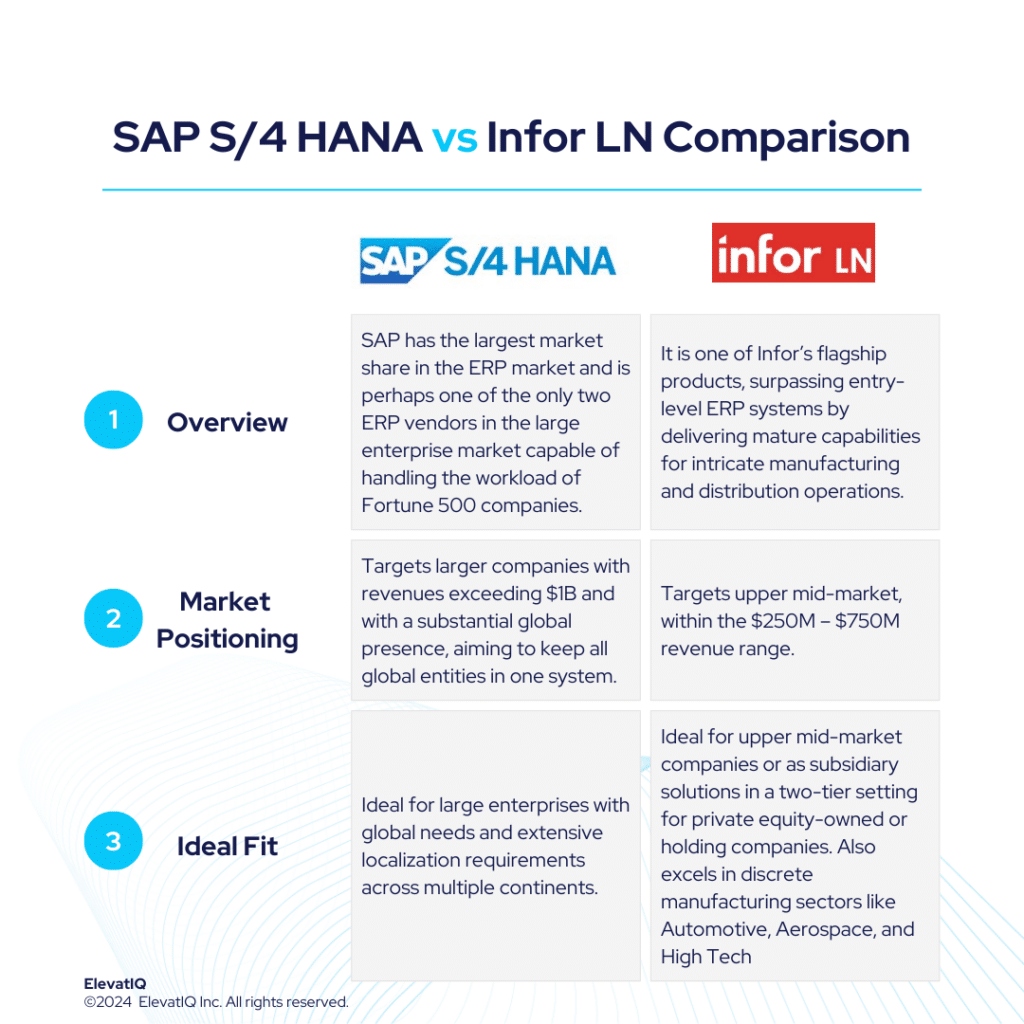
5. SAP S/4 HANA
SAP S/4 HANA has a positioning very similar to Oracle Cloud ERP. It is a slightly larger product designed for global financial consolidation, accommodating many different business models and processes within the same solution. When end-to-end traceability is required, but industry-specific capabilities are not a priority, SAP S/4 HANA is a better fit. It may not suitable SMB manufacturing companies without internal IT maturity. Thus, positioning itself at #5 spot in our list of top discrete manufacturing ERP systems.
Strengths
- ERP layers for complex organizations. The ERP layers are ideal for complex organizations, along with best-of-breed products like SuccessFactors or EWM. However, these solutions may not offer a tailored experience for specific industries. To achieve this, you will either need to customize the system or integrate additional add-ons.
- Diversity of the solution supports most discrete industries. The diversity of the solution allows you to support many different business models, although tailored capabilities for specific discrete verticals might not be as detailed.
- Global compliance and localization. The global compliance and localization capabilities of SAP S/4HANA are very similar to Oracle Cloud ERP.
Weaknesses
- Last mile capabilities through third-party vendors. The last mile or discrete-specific capabilities you acquire will be through third-party vendors. This approach increases vendor risk when utilizing these capabilities.
- Expensive implementations. The implementation is going to be slightly more expensive with SAP S/4 HANA just because the solution is large and designed to be highly scalable, requiring increased implementation efforts.
- Requires a mature internal IT team. SAP S/4 HANA also requires a very mature internal IT team to tailor, customize, and configure these capabilities.
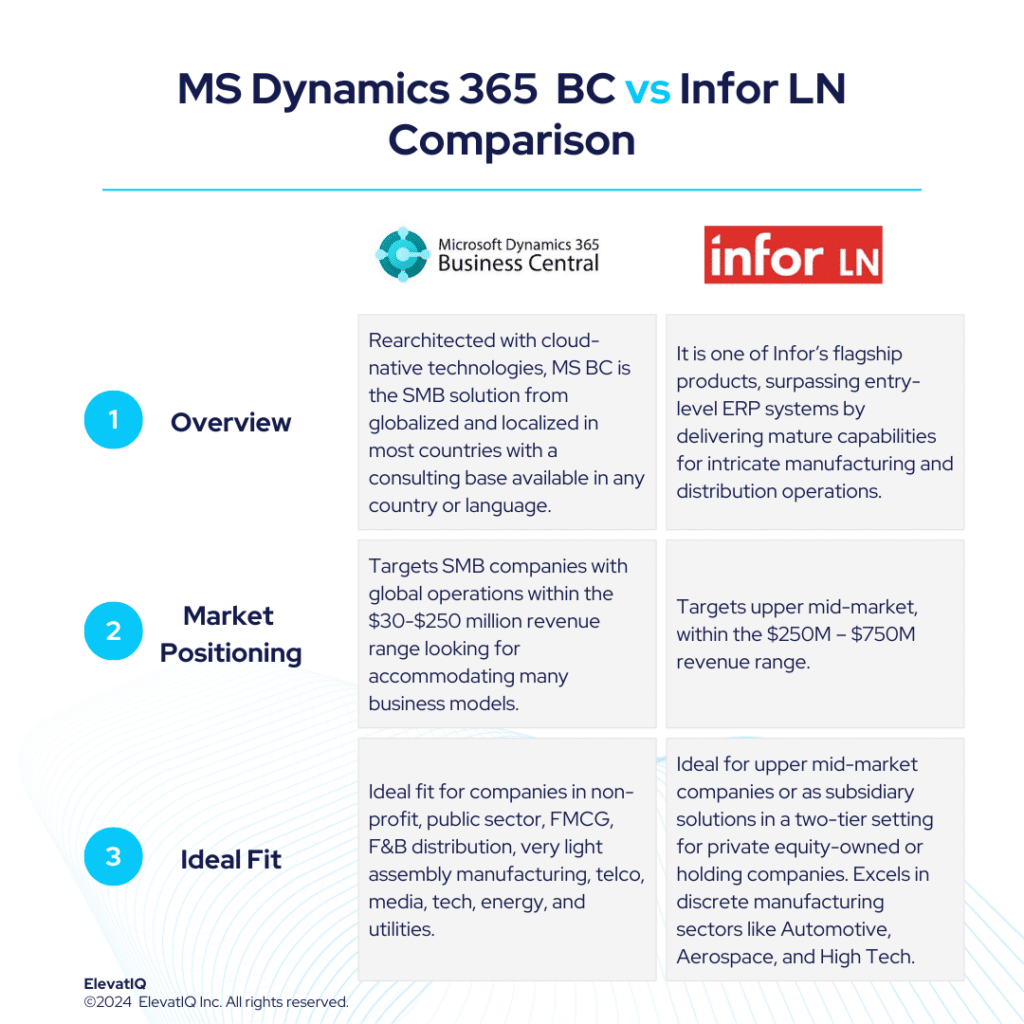
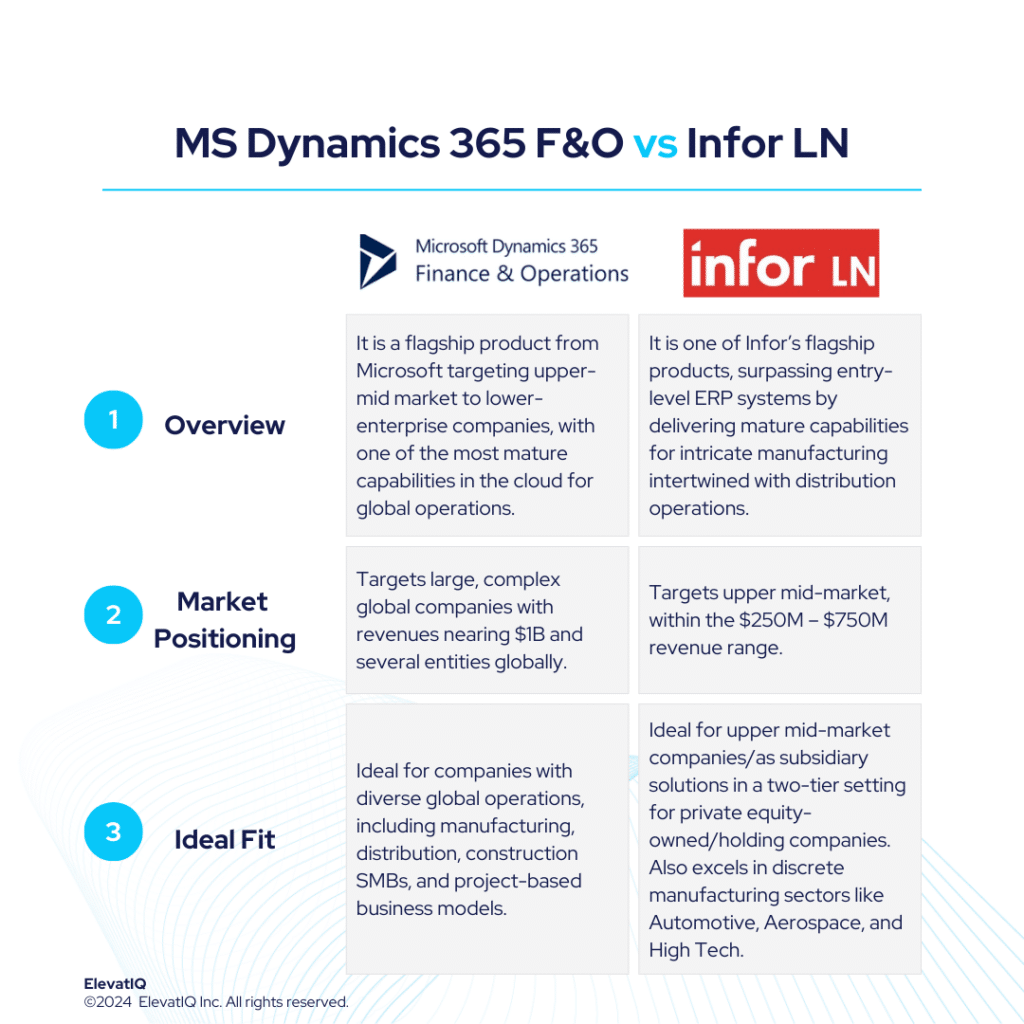
4. Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O
With a very similar positioning to Oracle Cloud ERP or SAP HANA, Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O is slightly more generalized and comparatively smaller in size. It may not be as proven with Fortune 500 workloads, as well as its extensive approval layers and organizational structures might not be as relevant for mid-market companies. With slightly superior cloud capabilities, it has an ecosystem that makes it suitable for private equity and holding companies aiming to streamline their portfolio companies on one solution. SMBs, however, might find its complex data model overwhelming. Thus, resulting in the placement of the product at the #4 spot in our list of top discrete manufacturing ERP systems.
Strengths
- Comprehensive localization across the globe. This would be beneficial for global discrete companies seeking synergies among their entities.
- Ecosystem. One of the most active ecosystems, offering numerous solutions to support various industries, even if those capabilities aren’t part of the core ERP layers or products.
- Development platform and Azure. It is also slightly more customizable just because of the development platform and the layers you have exposed for the customization.
Weaknesses
- Last mile capabilities through third-party vendors. The last mile or industry-specific capabilities you acquire will be through third-party vendors. This approach increases vendor risk when utilizing these capabilities.
- Expensive implementation. The implementation may be slightly more expensive because you’re dealing with many different vendors and many different add-ons.
- Requires mature internal IT teams. Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O also requires a mature internal IT team to tailor, customize, and configure these capabilities.
3. Infor CloudSuite Industrial (Syteline)
Infor CloudSuite Industrial (Syteline) is the SMB product from Infor. It’s designed for companies with engineer-heavy discrete manufacturing without mandating formal engineering processes, such as requiring revision numbers or strict change control. If your organization has more flexible engineering processes, you will find Infor CloudSuite Industrial much more enjoyable. While possessing hybrid manufacturing features, it falls short in global trade compliance and lacks support for manufacturers heavily involved in distribution-centric processes. Thus, grabbing its #3 spot in our list of top discrete manufacturing ERP systems.
Strengths
- Engineering-friendly for BOMs and costing. It’s designed for engineering-driven companies that have fluid engineering processes instead of formal processes. From the CSI perspective, the BOMs are complex manufacturing friendly, as the layers are far deeper and scalable compared to the other products.
- Embedded field services process. This would be helpful for discrete companies with field service-centric business models where field service processes need to overlap with production processes such as scheduling.
- Embedded quality processes. This would be beneficial for companies aiming to centralize their quality processes across all touch points including inbound, outbound, and in-process.
Weaknesses
- WBS-centric discrete processes. Not a better fit for discrete companies with project-centric operations, even though CSI has some project manufacturing capabilities.
- Not friendly for industries with complex inventories such as metal or medical devices. The core model includes attributes only for reporting and doesn’t account for them as part of core transactions such as planning, and scheduling.
- Legacy technology. The interface of Infor CloudSuite Industrial (Syteline) is still very legacy and generally, users report a steep learning curve with CSI.
2. Epicor Kinetic
Epicor Kinetic targets small-to-mid-size discrete manufacturers specializing in industries with formal engineering processes and complex inventory needs, such as automotive, aerospace, metal fabrication, and medical devices. It is equally adept at handling project-centric operations and distribution processes for discrete manufacturers with hybrid business models. However, despite recent developments, Epicor Kinetic might not be the best fit for companies with global financial operations and extensive field service operations. Thus, acquiring #2 spot on our list of top discrete manufacturing ERP systems.
Strengths
- Complex inventory. For example, medical devices and automotive, all of these industries require attributes as part of the product model, which are not only used for reporting but also mission-critical capabilities such as scheduling.
- Friendly for discrete companies heavy on distribution. Distribution-centric planning is included as part of the product. Ideal for companies with a business model that includes manufacturing plus distribution processes.
- Formal engineering governance. Industries such as aerospace that are very rigid about change control and revision numbers can benefit from these capabilities.
Weaknesses
- Not friendly for companies without revision numbers. The companies with ad-hoc BOMs and informal processes might struggle with mandated revision number of this product.
- Field service and quality processes not as embedded. Field service processes as well as quality processes are not embedded as part of the product, posing challenges in centralizing processes for all quality touch points.
- Weaker core accounting and finance layers. Finance and accounting layers are not going to be as strong as some of the other products that are on this list.
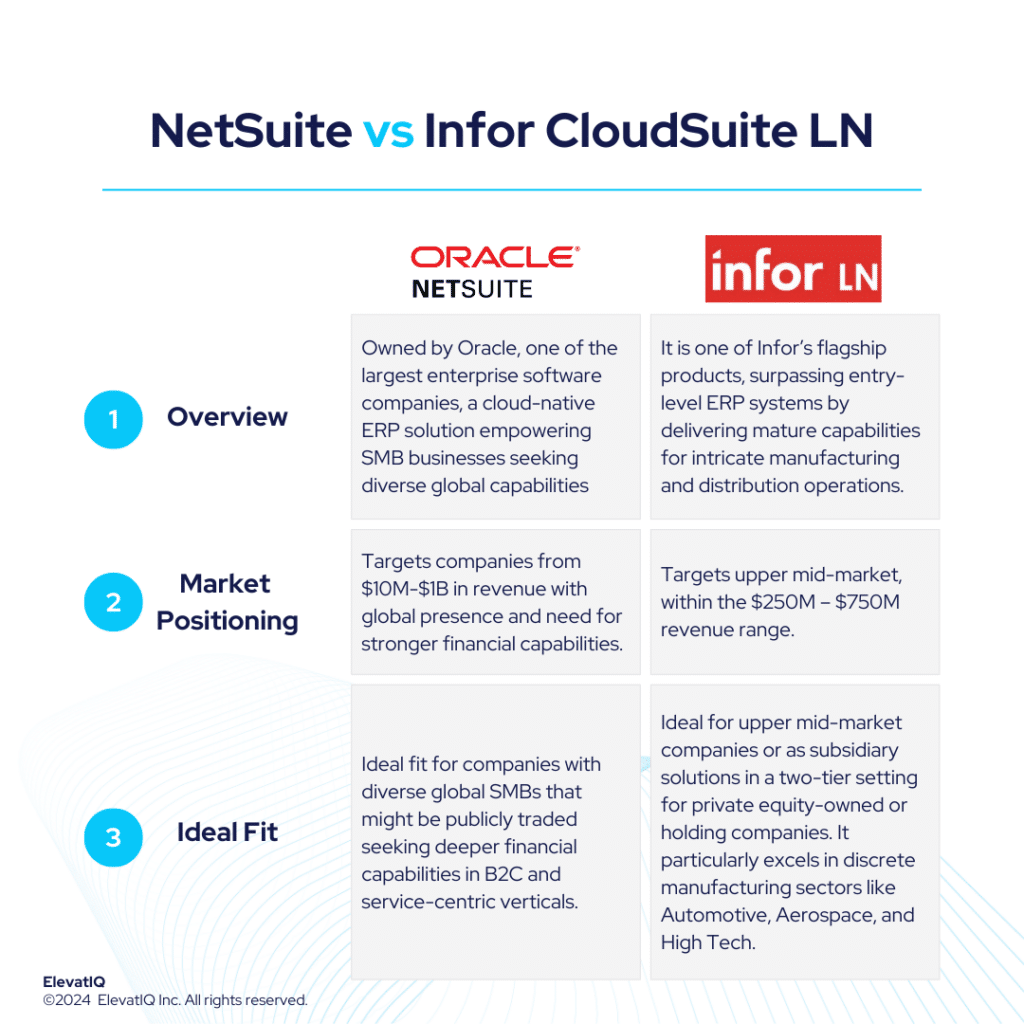
1. Infor CloudSuite LN
Infor CloudSuite LN is designed for discrete manufacturing companies that require diversified support for different discrete business models globally. It is one of the most comprehensive suites among the solutions on this list. While other solutions may claim mixed-mode manufacturing capabilities or extensive suite components, they are often limited in specific manufacturing types or product types. In contrast, CloudSuite LN can cover a wide range of options, including discrete manufacturing and distribution. Thus, acquiring #1 spot on our list of top discrete manufacturing ERP systems.
Strengths
- Comprehensive discrete capabilities. It is designed for discrete manufacturing companies with diverse business business models containing different mode types.
- Pre-integrated suite. The suite is tailored and flavored with industry-specific best-of-breed tools such as CAD and PLM, maintained and supported by Infor.
- Global capabilities. Compared to other smaller products such as Epicor Kinetic or Infor CSI, Infor CloudSuite LN can natively support more than 30 countries for companies seeking global operational synergies among entities.
Weaknesses
- Expensive. The license is likely to be perceived as expensive by smaller companies as the enterprise layers included might not be as relevant for them.
- Not suitable for SMBs below $250M in revenue. Not sold to smaller companies. Infor might push companies to smaller products such as CSI. Going outside of Infor might be a better choice in such scenarios as they might be able to match some layers of LN for smaller companies.
- Ecosystem. The ecosystem and consulting base is fairly limited as with most prescriptive products.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the landscape of discrete manufacturing ERP systems is vast and varied, catering to the unique needs of companies involved in producing distinct items through assembly processes. From robust supply chain management to intricate inventory control, these systems play a critical role in optimizing production efficiency and ensuring compliance. Each ERP solution offers its strengths and weaknesses, with considerations ranging from technological sophistication to industry-specific functionality.
As we’ve explored the top 10 discrete manufacturing ERP systems for 2024, it’s evident that the ideal choice depends on factors such as company size, industry focus, and operational complexity. By aligning ERP selection with specific business requirements, organizations can harness the power of these systems to drive growth and streamline operations. While this list offers valuable insights, seeking advice from an independent ERP consultant can greatly enhance your implementation success.